Power Retaining Blocks
Retaining Blocks
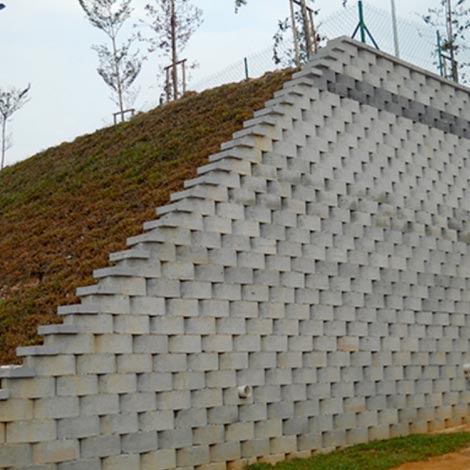

Advantages

Prevents Soil Erosion.

Highly Durable.

Fire & heat Resistant

Economical

Built-in drainage systems

Environment friendly
| Technical Details | |
|---|---|
| Types | Rectangular, Interloacking, Half Round, Tongue and Groove, etc. |
| Colour | Grey. |
| Weight | 30 to 200 Kg (Depending upon the size and shape). |
| Water Absorption | 4 to 6 % weight of the block |
| Compressive Strength | 8-40 Mpa |
| Vibration Frequency | 50-90 Hz |
| Material Compaction System | Dual Vibration + Pressure Based. |
Steps for laying Power Retaining Blocks
- The site should be cleared of any vegetation or debris, and the area should be levelled and compacted to provide a stable base for the retaining wall.
- Excavate the area where the retaining wall will be built to the depth required by the retaining blocks and the design specifications.
- A layer of crushed stone or gravel should be placed at the bottom of the excavation to provide drainage and prevent water from collecting behind the wall.
- A geotextile fabric should be placed over the drainage layer to prevent soil from mixing with the drainage layer and to provide stability.
- The retaining blocks should be laid on the substrate, starting at the bottom and working up to the desired height. The blocks should be stacked in a running bond pattern, with the interlocking features facing outwards, and should be levelled and plumb.
- If necessary, retaining blocks can be cut to fit specific dimensions using a masonary saw or other appropriate cutting tools.
- The area behind the retaining wall should be backfilled with soil or other material and compacted to provide stability to the wall.
- The joints between the retaining blocks should be filled with sand or a suitable jointing material to prevent the blocks from moving and to provide a stable surface.
- A vibrating plate compactor or similar tool can be used to compact the retaining blocks and the jointing material to ensure a stable and durable surface.
Application Procedure of Retaining Blocks
Site Preparation: The site should be cleared of any vegetation or debris, and the area should be levelled and compacted to provide a stable base for the retaining wall.
Excavation: Excavate the area where the retaining wall will be built to the depth required by the retaining blocks and the design specifications.
Installation of Drainage Layer: A layer of crushed stone or gravel should be placed at the bottom of the excavation to provide drainage and prevent water from collecting behind the wall.
Installation of Geotextile Fabric: A geotextile fabric should be placed over the drainage layer to prevent soil from mixing with the drainage layer and to provide stability.
Laying of Retaining Blocks: The retaining blocks should be laid on the substrate, starting at the bottom and working up to the desired height. The blocks should be stacked in a running bond pattern, with the interlocking features facing outwards, and should be levelled and plumb.
Cutting of Retaining Blocks: If necessary, retaining blocks can be cut to fit specific dimensions using a masonary saw or other appropriate cutting tools.
Backfill: The area behind the retaining wall should be backfilled with soil or other material and compacted to provide stability to the wall.
Jointing of Retaining Blocks: The joints between the retaining blocks should be filled with sand or a suitable jointing material to prevent the blocks from moving and to provide a stable surface.
Compact the Retaining Blocks: A vibrating plate compactor or similar tool can be used to compact the retaining blocks and the jointing material to ensure a stable and durable surface.
Area of Application


Retaining Walls, Garden and Landscaping for Raised Beds, Driveway and Path retaining
Safety Measures


Safety Measures While Fixing Retaining Blocks
- When fixing retaining blocks, it’s important to take the following safety measures:
- 1. Personal protective equipment: Always wear the appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses, gloves, safety shoes and a hard hat, to protect yourself from injury.
- 2. Tools: Make sure you have the correct tools for the job, and that they are in good condition.
- 3. Lifting techniques: Use proper lifting techniques to avoid injury when handling heavy blocks. Get help from a second person if necessary.
- 4. Stabilization: Make sure the retaining wall is properly stabilized to prevent it from collapsing during construction.
- 5. Working at height: If working at height, use a ladder or scaffold that is securely anchored and in good condition.
- 6. Support: Make sure the retaining wall is properly supported during construction, especially when adding additional courses of blocks.
- 7. Site inspection: Inspect the site regularly to ensure that it is safe and that the retaining wall is being constructed correctly.
By taking these safety measures, you can reduce the risk of injury and ensure that the retaining wall is constructed safely and correctly.
